Oxytocin
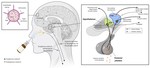
An accumulating body of evidence demonstrates the crucial role of the neuropeptide hormone oxytocin in the modulation of social cognition and behaviour. However, oxytocin is more than just a “social” neuropeptide as it’s also involved in the regulation of a number of other physiological systems. Indeed, oxytocin system dysfucntion may contribute to the overrepresentation of metabolic disorders in severe mental illnesses. Remarkably, little work has explicitly investigated how the impact of oxytocin on physiology influences cognition and behaviour. Moreover, the role of oxytocin gene pathway variants on psychological and physiological processess is poorly characterised. A better understanding of how the oxytocin system influences the brain and body can help unravel the neurobiological basis of human cognition, and how this is linked to various physiological processes.
Daniel S. Quintana
Associate Professor
Investigating biological systems that link psychosocial factors to health, with a focus on neuroendocrine systems and the autonomic nervous system.
Related
- Improving the precision of intranasal oxytocin research
- Rethinking Oxytocin’s role in cognition
- Oxytocin: How Does This Neuropeptide Change Our Social Behavior?
- The impact of oxytocin administration on brain activity: a systematic review and meta-analysis protocol
- Reliability of basal plasma vasopressin concentrations in healthy male adults